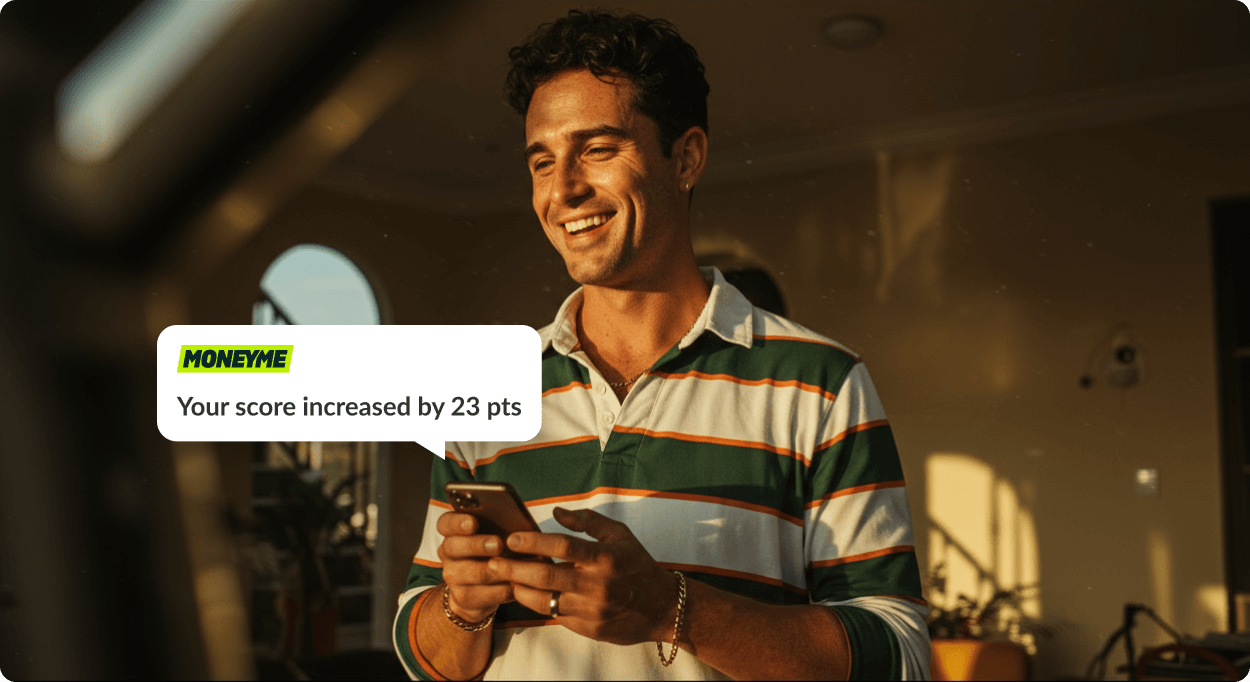
About MONEYME
Click on a category to see options
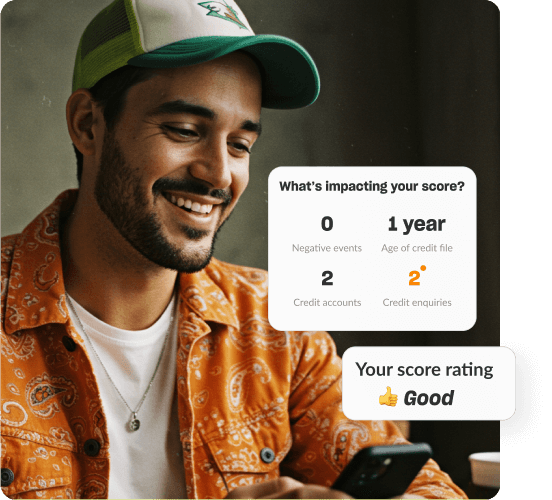
Get in-depth insights
See what's on your credit file, how it's impacting your score and what you can do about it.
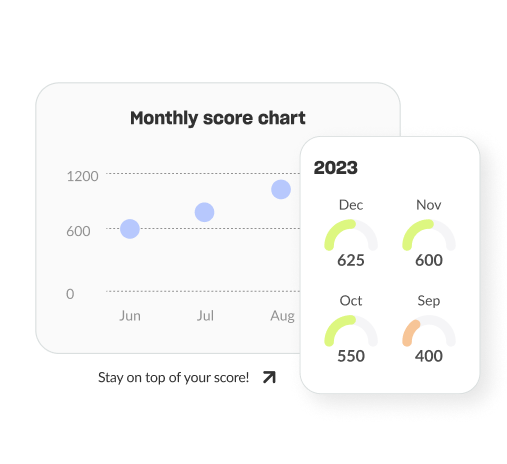
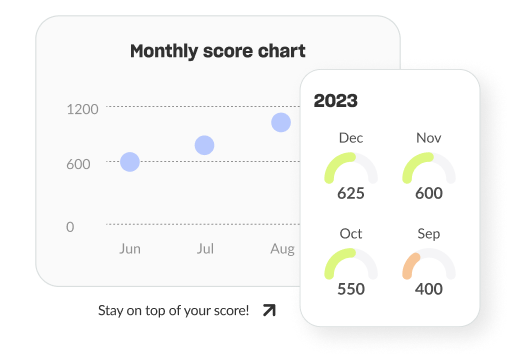
Track your progress
We keep track of your score history so you can see how your score changes over time. Watch it improve or spot when something has impacted it negatively.
Boost your knowledge
Learn all there is to know about credit scores. We share useful tips and tricks on how to boost your score, how to avoid the common mistakes that will tank it, and much more.

Check your credit score
The MONEYME app provides a fast and easy way to check your credit score in Australia, and it's completely free. Simply download the app, access your credit score and receive personalised insights to understand the factors that influence it.
Understanding how credit scores work in Australia
Your credit score reflects your past credit use, repayment history, and the credit accounts you currently have. Late or missed payments can lower your score, while a history of consistent, timely repayments can increase your score over time. In simple terms, a high credit score demonstrates your trustworthiness to lenders and can help you access better loan terms and a lower interest rate.
Benefits of monitoring your credit score
Here's how checking your credit score can help you take control of your finances:
- Understand your score: Getting to know your credit score helps you make smart decisions about loans, credit cards, and how you spend your money.
- Get better deals: Improving your credit score can help you get a better deal with lenders, like lower interest rates on loans, giving you more money in your pocket!
- Track your success: Watch your credit score rise as you improve your credit habits, and celebrate your achievements as you build a stronger financial future.
- Fraud protection: By keeping an eye on your credit score, you can spot any unauthorised activity right away and take action to protect yourself.
- Peace of mind: By understanding and improving your score, you're setting yourself up for better financial outcomes in the future, whether it's buying a home or starting a business.
With no impact to your credit score
Award-winning lender

What our customers say
MONEYME Reviews Average rating: 4.7, based on 4700 reviewsWith no impact to your credit score
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a number that demonstrates your credit history and financial habits. Lenders use this score to assess your risk as a borrower and determine whether or not to lend you money, and if so, at what interest rate. A higher credit score generally indicates a lower risk to the lender, which can result in more favourable loan terms.

Why choose MONEYME to check your credit score?
Find out why so many Australians choose our app to build brighter financial futures.
All-in-one app: The MONEYME app makes it simple to perform a free credit score check in Australia and explore other products.
User-friendly: Forget financial jargon and confusing products. We make understanding your credit score easier than ever.
Personalised insights: Get more than just a score. Use our in-depth insights and actionable advice to boost your creditworthiness.
Trusted by thousands: Join thousands of Australians on the MONEYME app.
A sustainable choice: MONEYME is committed to using business as a force for good and meeting high social and environmental standards..
Purpose-driven
and responsible
At MONEYME, we're not just here to provide low rate loans - we're here to make a difference. We believe in providing smart, responsible lending that keeps you financially on track, whilst doing good for the planet.
As a Certified B CorporationTM we're big on sustainability. We hold ourselves accountable to the high standards of the B Corp movement, supporting renewable energy projects, doing our part for the community, and striving towards a greener future.
Explore our impact
*This comparison rate is based on an unsecured variable rate personal loan of $30,000 for a term of 5 years. Rates displayed are for customers with an excellent credit history, where a $0 establishment fee applies. For other borrowers, an establishment fee of $395 or $495 will apply, based on loan amount. A $10 monthly fee applies to all personal loans. WARNING: This comparison rate is true only for the example given and may not include all fees and charges. Different terms, fees or other loan amounts might result in a different comparison rate.